Using MPEA and oxygen electrode for the first time to prove that the active ingredient of sunscreen "oxybenzophenone" severely inhibits photosynthesis & respiration of higher plant leaves
Welcome to the "Lufthansa Technology Group" WeChat public number! Official website: 
Oxybenzone is a major active ingredient of most UV sunscreens. It has also been widely added to many personal care products. Recently, some scholars have reported that it can cause bleaching of corals, leading to abnormalities in animal hormone secretion, embryo development and reproductive fertilization. Therefore, recently the United States of Hawaii and many countries along the island countries passed laws prohibiting the use of oxybenzone-containing sunscreen. 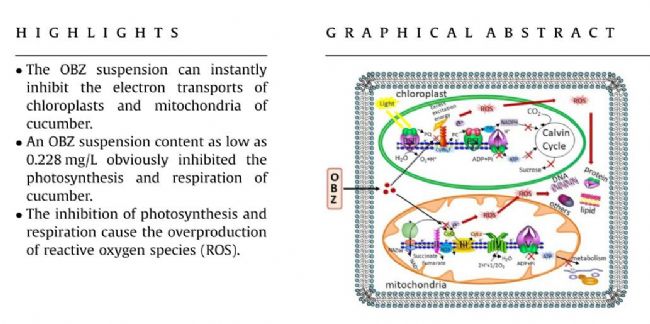 So far, research on oxybenzone has focused on animals and humans. It is not known whether oxybenzone is the most important metabolic process for higher plants - whether photosynthesis and respiration have an effect.
So far, research on oxybenzone has focused on animals and humans. It is not known whether oxybenzone is the most important metabolic process for higher plants - whether photosynthesis and respiration have an effect.
Recently, Professor Li Qingming, a member of the Shandong Agricultural University Horticultural College, and a team of professors from the Shandong University of Agriculture and Biosciences , Gao Huiyuan , teamed up with the M-PEA multi-functional plant efficiency analyzer manufactured by Hansatech , UK , and Oxytherm oxygen electrodes to study different levels of oxybenzene . The effects of ketone suspension on photosynthesis, respiration and chlorophyll fluorescence of cucumber leaves, and the transient inhibition of chloroplast photosynthetic electron transport and mitochondrial respiratory electron transport.  This study revealed for the first time that oxybenzone has a significant inhibitory effect on photosynthesis and respiration of higher plants. Moreover, very low levels of oxybenzone (0.228 mg / L) can immediately inhibit the electron transport of chloroplasts and mitochondria. This suggests that oxybenzone is harmful to all organisms (with respiration).
This study revealed for the first time that oxybenzone has a significant inhibitory effect on photosynthesis and respiration of higher plants. Moreover, very low levels of oxybenzone (0.228 mg / L) can immediately inhibit the electron transport of chloroplasts and mitochondria. This suggests that oxybenzone is harmful to all organisms (with respiration).
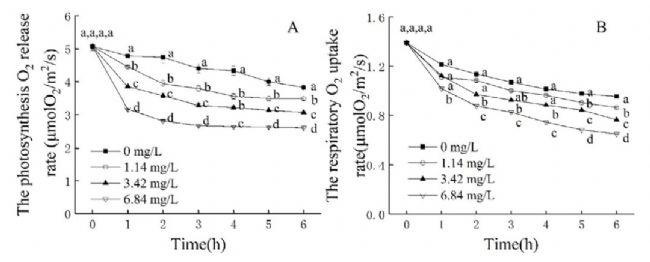 Figure 1: Inhibition of photosynthesis (A) and respiration (B) in cucumber leaves with different oxybenzone content suspensions.
Figure 1: Inhibition of photosynthesis (A) and respiration (B) in cucumber leaves with different oxybenzone content suspensions.
Due to the inhibition of photosynthetic electron transfer, the excess excitation energy in plant leaves is greatly increased, resulting in a large accumulation of active oxygen. The accumulated active oxygen will further damage the biomacromolecules such as photosynthetic apparatus, cell membrane, DNA and protein. 
Figure 2. Effect of different levels of oxybenzone on chlorophyll fluorescence of cucumber leaves after 1 hour of oxybenzone treatment. A: Vt curve, B: ΔVt curve, C: fluorescence parameter. 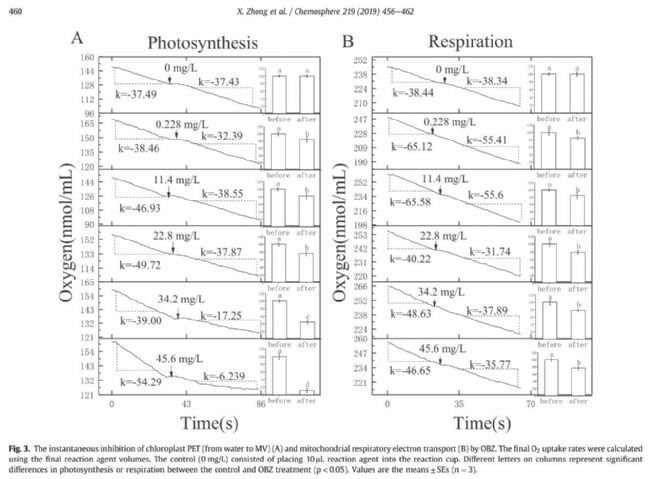 Figure 3: Instantaneous inhibition of photosynthetic electron transport (A) and mitochondrial respiratory electron transport (B) in cucumber chloroplasts with different levels of oxybenzone suspension.
Figure 3: Instantaneous inhibition of photosynthetic electron transport (A) and mitochondrial respiratory electron transport (B) in cucumber chloroplasts with different levels of oxybenzone suspension. 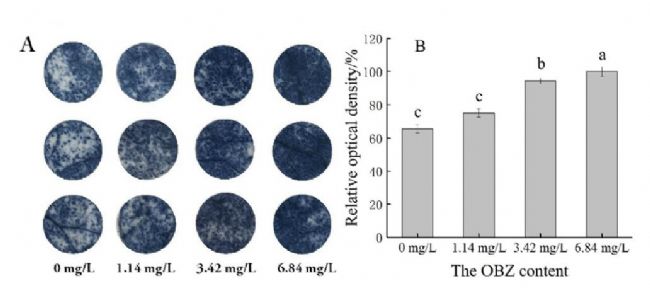
Figure 4: Effect of different levels of oxybenzone suspension on the production of reactive oxygen species in cucumber leaves
The paper was published in the environmental journal Topo Chemosphere. Once published, it has attracted the attention of environmental scientists around the world. The results of this study provide scientific evidence for the damage of oxybenzone to plants (and organisms) and provide strong support for the use of oxybenzone and the protection of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
Literature download address: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1669o_EW49Sk-322P5Yt6LA Extraction code: 7vhv
Food Grade Phosphate,Dimagnesium Phosphate,Iron Pyrophosphate Powder,Ferric Diphosphate
Wuxi Yangshan Biochemical Co.,Ltd. , https://www.yangshanchem.com