Article introduction
LncRNA is a long-chain non-coding RNA with a length greater than 200 nt and plays an important role in the regulation of different molecules. Its main function is not only to bind to functional proteins, but also to regulate gene expression at the transcriptional or post-transcriptional level, and lncRNA can also act as a bait to adsorb miRNA and regulate the expression of target genes regulated by miRNA. However, the current understanding of the expression profile and biological function of lncRNA in gastric cancer is still limited; in this study, the author first analyzed the lncRNA microarray database of gastric cancer by bioinformatics, and found that LINC0034 was highly expressed in gastric cancer, and it was associated with gastric cancer. Clinically relevant, the results showed that LINC00346 was repeatedly up-regulated in gastric cancer, and its expression was positively correlated with pathological stage, tumor volume, and poor prognosis. Then explored the in vitro and in vivo functions of LINC00346, experiments show that LINC00346 can affect the biological functions of gastric cancer growth, migration and invasion. The authors also explored the upstream and downstream molecular mechanisms of LINC00346 regulation of gastric cancer development. The upstream mechanism showed that the oncogenic transcription factors KLF5 and MYC can bind to the LINC00346 promoter and enhance its expression. The downstream mechanism shows that LINC00346 is mainly expressed in the cytoplasm and can be through the ceRNA mechanism. As a molecular sponge of miR-34a-5p, it regulates the expression of downstream target genes CD44, AXL, NOTCH1 and regulates the biological functions of gastric cancer cells by adsorbing miR-34a-5p.
In summary, the results of this study demonstrate that KLF5, MYC/LINC00346/miR-34a-5p play a key role in the development of gastric cancer, providing a new direction and ideas for the treatment of gastric cancer.
LncRNA is a long-chain non-coding RNA with a length greater than 200 nt and plays an important role in the regulation of different molecules. Its main function is not only to bind to functional proteins, but also to regulate gene expression at the transcriptional or post-transcriptional level, and lncRNA can also act as a bait to adsorb miRNA and regulate the expression of target genes regulated by miRNA. However, the current understanding of the expression profile and biological function of lncRNA in gastric cancer is still limited; in this study, the author first analyzed the lncRNA microarray database of gastric cancer by bioinformatics, and found that LINC0034 was highly expressed in gastric cancer, and it was associated with gastric cancer. Clinically relevant, the results showed that LINC00346 was repeatedly up-regulated in gastric cancer, and its expression was positively correlated with pathological stage, tumor volume, and poor prognosis. Then explored the in vitro and in vivo functions of LINC00346, experiments show that LINC00346 can affect the biological functions of gastric cancer growth, migration and invasion. The authors also explored the upstream and downstream molecular mechanisms of LINC00346 regulation of gastric cancer development. The upstream mechanism showed that the oncogenic transcription factors KLF5 and MYC can bind to the LINC00346 promoter and enhance its expression. The downstream mechanism shows that LINC00346 is mainly expressed in the cytoplasm and can be through the ceRNA mechanism. As a molecular sponge of miR-34a-5p, it regulates the expression of downstream target genes CD44, AXL, NOTCH1 and regulates the biological functions of gastric cancer cells by adsorbing miR-34a-5p.
In summary, the results of this study demonstrate that KLF5, MYC/LINC00346/miR-34a-5p play a key role in the development of gastric cancer, providing a new direction and ideas for the treatment of gastric cancer.

Published issue: Cell Death & Differentiation
Impact factor: 8.0
Experimental methods: Advanced analysis of biomarkers , transcriptome RNA sequencing , RIP , pulldown (provided by Cloud Sequence Bio)
Sequencing samples: gastric cancer cells overexpressing LINC00346 (experimental group), gastric cancer cells transfected with empty plasmids (control group)
Impact factor: 8.0
Experimental methods: Advanced analysis of biomarkers , transcriptome RNA sequencing , RIP , pulldown (provided by Cloud Sequence Bio)
Sequencing samples: gastric cancer cells overexpressing LINC00346 (experimental group), gastric cancer cells transfected with empty plasmids (control group)
Article content
1. Bioinformatics analysis of gastric cancer lncRNA microarray database, now LINC0034 is highly expressed in gastric cancer, and has clinical relevance to gastric cancer
Experimental route
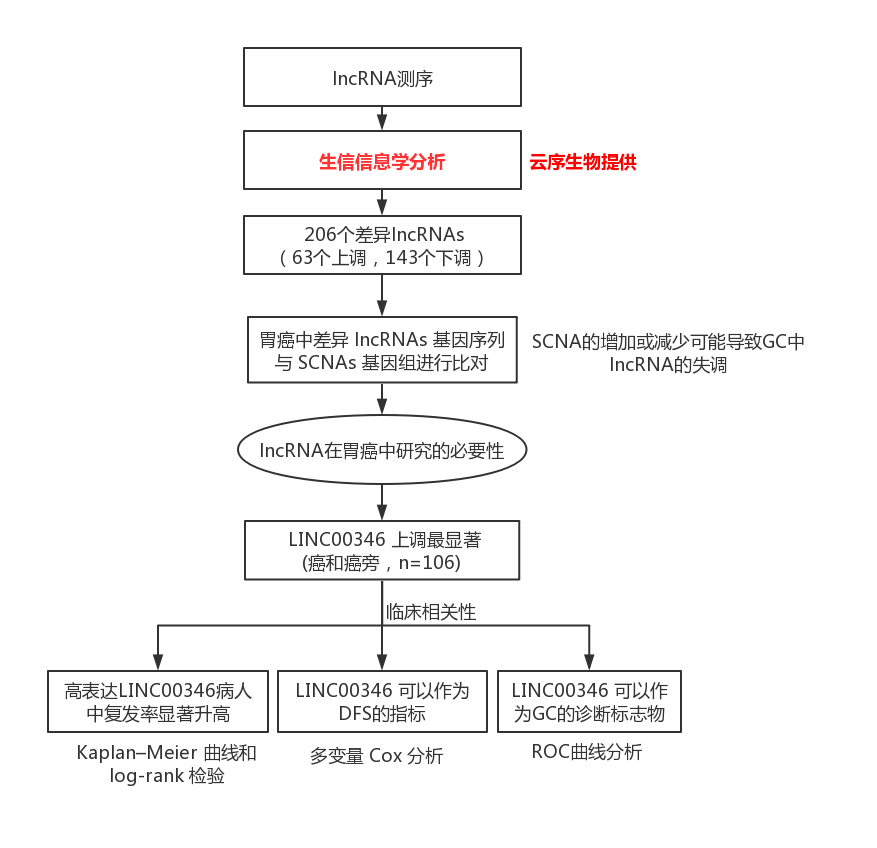
Results: LINC0034 has clinical relevance of gastric cancer
a, b: LINC0034 was highly expressed in gastric cancer; the expression of cd:LINC0034 was positively correlated with pathological stage, large tumor volume and poor prognosis.
a, b: LINC0034 was highly expressed in gastric cancer; the expression of cd:LINC0034 was positively correlated with pathological stage, large tumor volume and poor prognosis.

2. Exploring the in vitro and in vivo functions of LINC00346 in gastric cancer
Experimental route
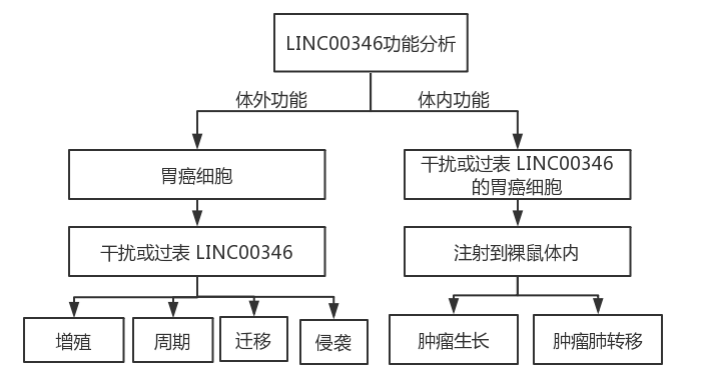
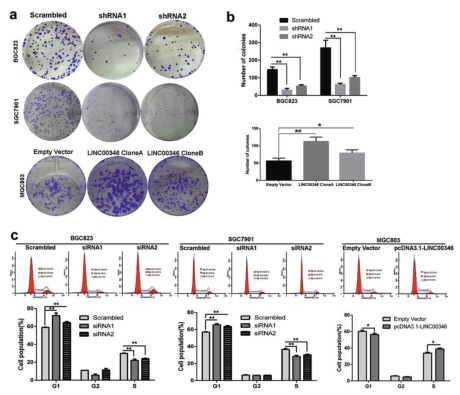
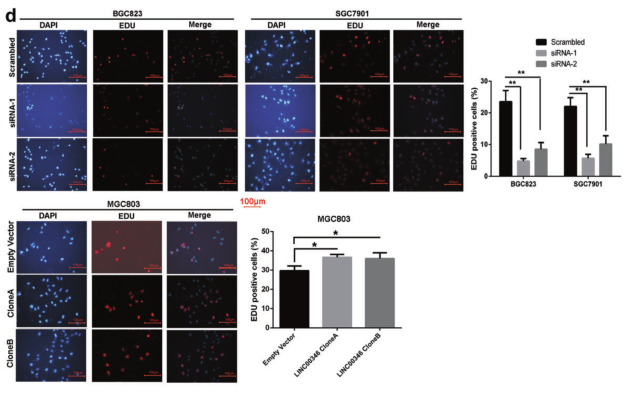
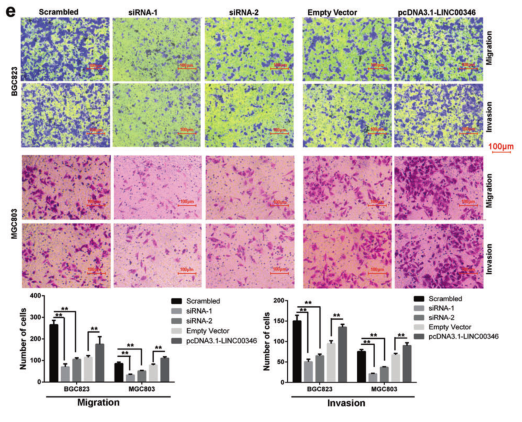
Results 1: In vitro study of the effect of LINC00346 on proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells
Ab. Clonal formation experiments explore cell proliferation; c. Flow cytometry experiments to explore cell cycle tissue; d. EDU immunofluorescence staining experiments to explore cell proliferation; e. Transwell and invasion experiments to explore cell migration and invasion ability.
Ab. Clonal formation experiments explore cell proliferation; c. Flow cytometry experiments to explore cell cycle tissue; d. EDU immunofluorescence staining experiments to explore cell proliferation; e. Transwell and invasion experiments to explore cell migration and invasion ability.
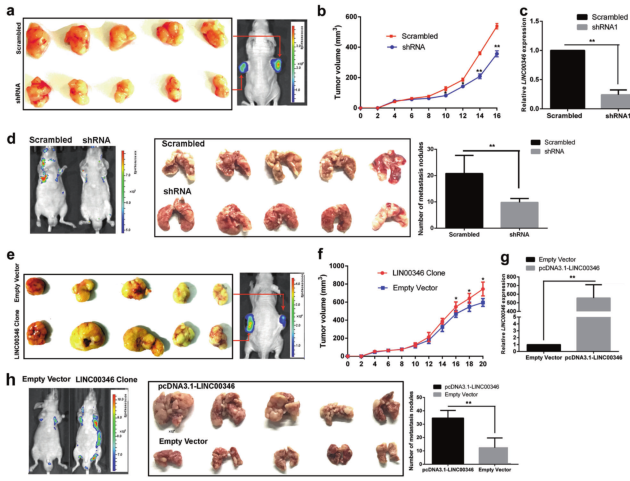
Results 2: In vivo investigation of the effect of LINC00346 on the growth and metastasis of gastric cancer in vivo
Ah: nude mice tumor formation experiment
Ah: nude mice tumor formation experiment
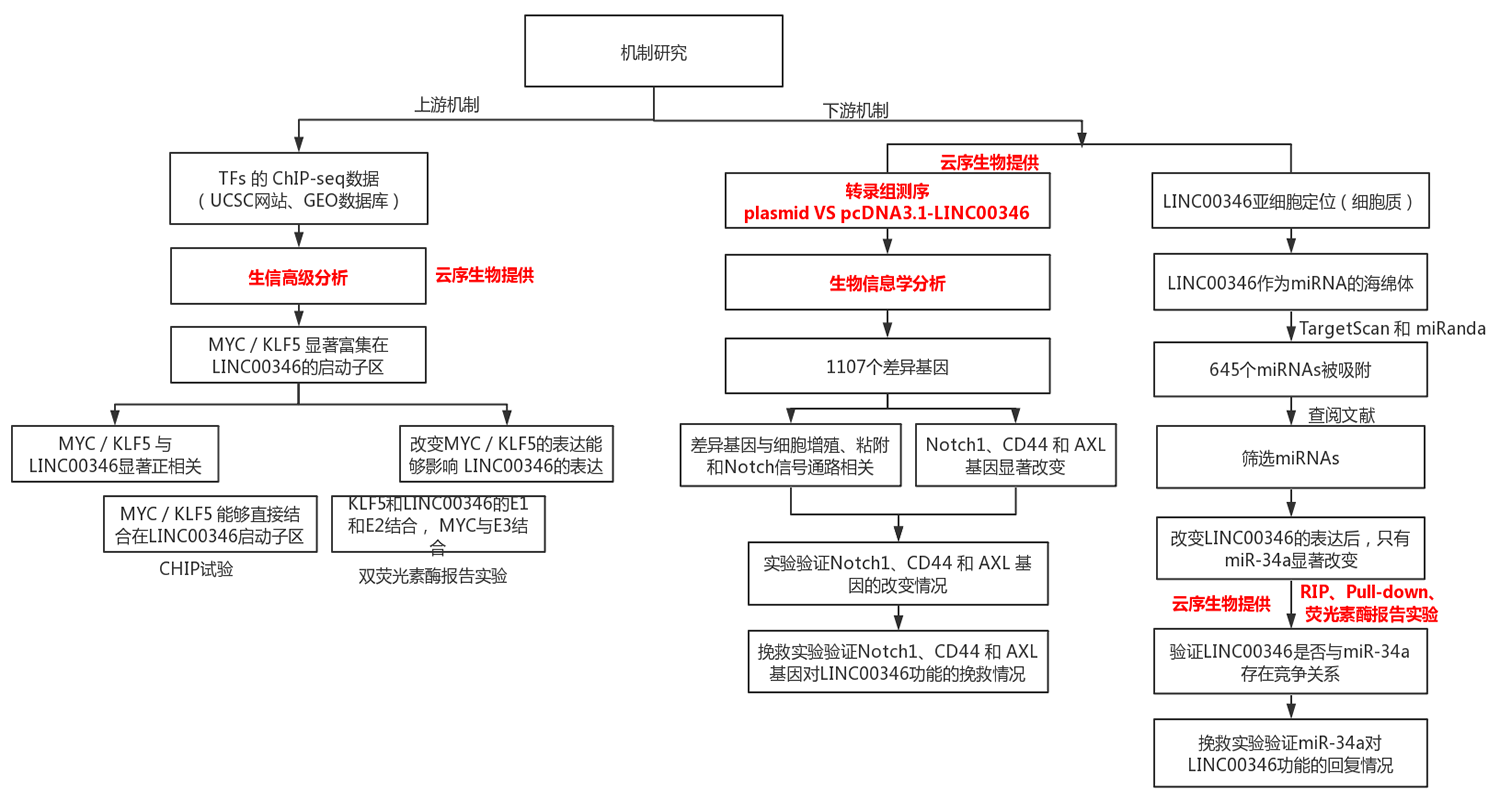
3. Exploring the upstream and downstream molecular mechanisms of LINC00346 regulating gastric cancer development
Experimental route
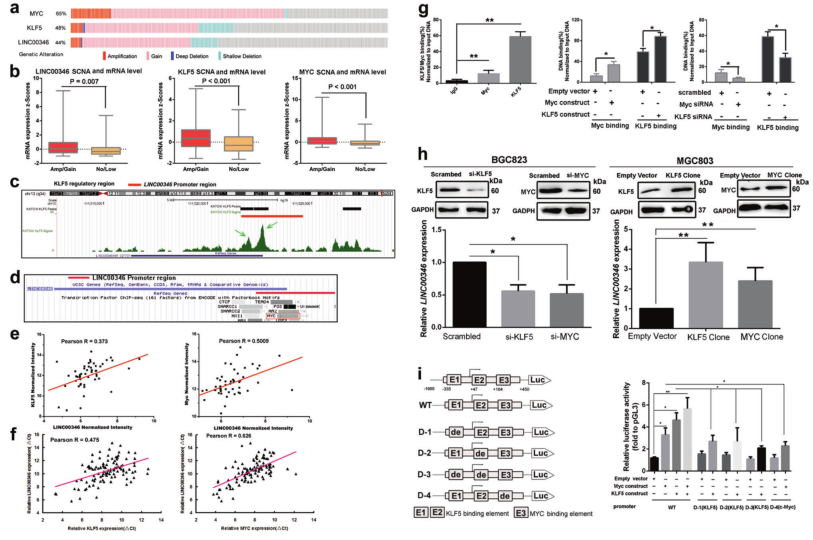
(1) LINC00346 regulates the upstream mechanism of gastric cancer development <br> Results: The transcription factors KLF5 and MYC bind to the LINC00346 promoter and enhance its expression.
a. Oncoprint analysis of transcription factors MYC, KLF5 and LINC00346; b. Expression of transcription factors KLF5, MYC, LINC00346 with or without gastric cancer KLF5/ MYC / LINC00346 SCNAs; c. Analysis of GSE51705 database, KATO-III GC KLF5 binds to the LINC00346 gene promoter in the cell; d. UCSC genomic bioinformatics website shows that MYC is highly enriched in the promoter of LINC00346; e. GSE51575 database shows that the expression of LINC00346 is positively correlated with KLF5 or MYC; f. qPCR display The expression of LINC00346 was positively correlated with KLF5 or MYC; g. ChIP experiments showed that endogenous MYC and KLF5 bind to the promoter region of LINC00346 gene. h. WB shows KLF5 and MYC protein expression after interference or overexpression of LINC00346; i. Dual fluorescence reporter assay detects LINC00346 promoter fragment directly binding to KLF5 or MYC
a. Oncoprint analysis of transcription factors MYC, KLF5 and LINC00346; b. Expression of transcription factors KLF5, MYC, LINC00346 with or without gastric cancer KLF5/ MYC / LINC00346 SCNAs; c. Analysis of GSE51705 database, KATO-III GC KLF5 binds to the LINC00346 gene promoter in the cell; d. UCSC genomic bioinformatics website shows that MYC is highly enriched in the promoter of LINC00346; e. GSE51575 database shows that the expression of LINC00346 is positively correlated with KLF5 or MYC; f. qPCR display The expression of LINC00346 was positively correlated with KLF5 or MYC; g. ChIP experiments showed that endogenous MYC and KLF5 bind to the promoter region of LINC00346 gene. h. WB shows KLF5 and MYC protein expression after interference or overexpression of LINC00346; i. Dual fluorescence reporter assay detects LINC00346 promoter fragment directly binding to KLF5 or MYC
(2) LINC00346 regulates the downstream mechanism of gastric cancer development
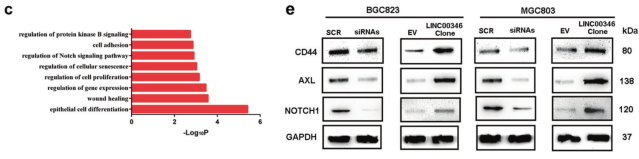
Results 1: GSEA and GO analysis LINC00346 high/low expression of gastric cancer patients and cells
a. GSEA analysis of GSE65801 data to compare the enrichment signal pathway of LINC00346 high/low differential gene; b. Heat map showing differential gene after overexpression of LINC00346 in gastric cancer; c. GO analysis of differential gene enrichment; d, e qPCR and WB screen for tumor-associated differential genes.
Results 1: GSEA and GO analysis LINC00346 high/low expression of gastric cancer patients and cells
a. GSEA analysis of GSE65801 data to compare the enrichment signal pathway of LINC00346 high/low differential gene; b. Heat map showing differential gene after overexpression of LINC00346 in gastric cancer; c. GO analysis of differential gene enrichment; d, e qPCR and WB screen for tumor-associated differential genes.
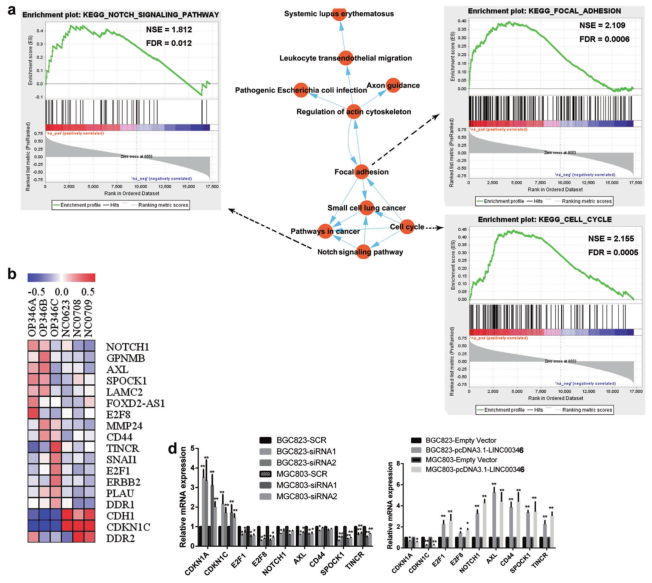
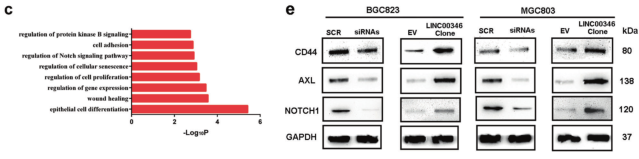
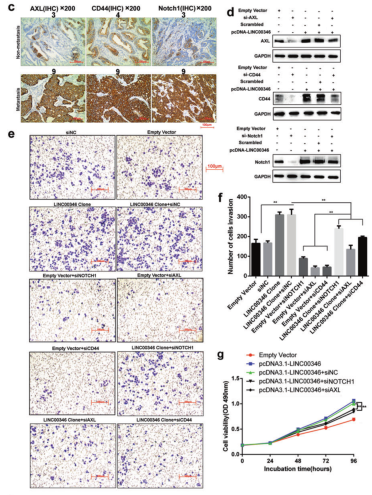
Results 2: LINC00346 promotes proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating Notch1, CD44 and AXL
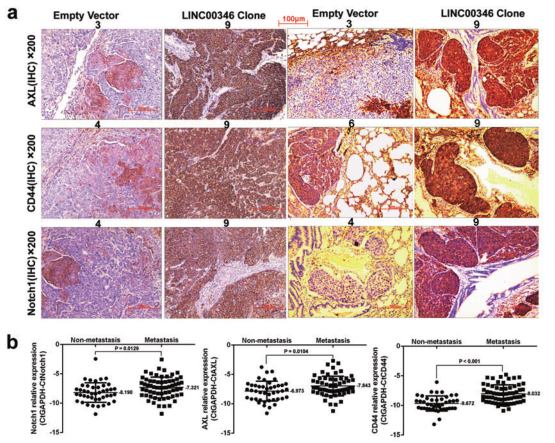
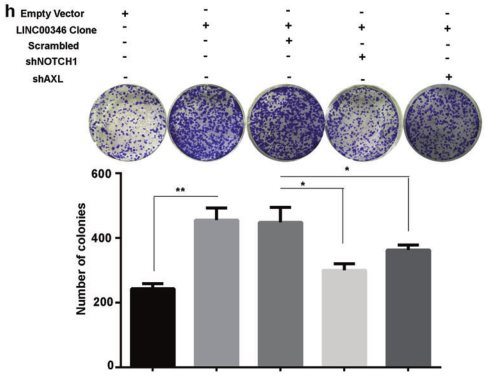
a. IHC analysis of expression of Notch1, CD44, and AXL in tumor tissues and tumor lung metastasis; b. qPCR detection of expression of Notch1, CD44, and AXL in gastric cancer with or without lymph node metastasis; c. IHC detection of gastric cancer or No expression of Notch1, CD44, and AXL in lymph node metastasis; d. WB detection of protein expression of Notch1, CD44, and AXL in gastric cancer cells; e, f. Transwell assay to detect the invasion of LINC00346 by Notch1, CD44 or AXL Ability; g. MTT and h. Cloning formation assays to test the ability of Notch1, CD44 or AXL to rescue the proliferation function of INC00346.
a. IHC analysis of expression of Notch1, CD44, and AXL in tumor tissues and tumor lung metastasis; b. qPCR detection of expression of Notch1, CD44, and AXL in gastric cancer with or without lymph node metastasis; c. IHC detection of gastric cancer or No expression of Notch1, CD44, and AXL in lymph node metastasis; d. WB detection of protein expression of Notch1, CD44, and AXL in gastric cancer cells; e, f. Transwell assay to detect the invasion of LINC00346 by Notch1, CD44 or AXL Ability; g. MTT and h. Cloning formation assays to test the ability of Notch1, CD44 or AXL to rescue the proliferation function of INC00346.
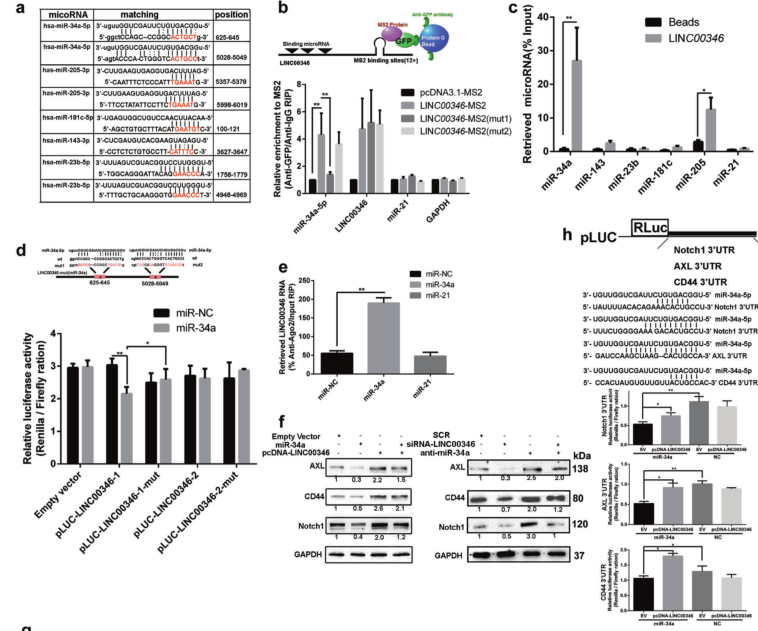
Results 3: LINC00346 regulates Notch1, CD44 and AXL by interacting with miR-34a-5p
a. LINC00346 and miRNA binding site prediction; b. MS2-RIP experiments verify LINC00346 can pull down miRNAs; c. Pull -down experiments verify LINC00346 adsorbed miRNAs; d. Double fluorescence reporter gene experiments miR-34a and LINC00346 directly Combining; e. AGO2 RIP experiments verify that miR-34a can pull down LINC00346; f. WB shows that miR-34a can rescue the regulation of protein levels of Notch1, CD44 or AXL by LINC00346; g. Tranwell experiments show that miR-34a can rescue LINC00346 pairs Regulation of migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells; h. Dual fluorescence reporter gene experiments show that miRNA can directly bind to the 3'UTR of Notch1, CD44 or AXL genes; i. In situ hybridization experiments show that LINC00346 and miR-34a can colocalize in cytoplasm in.
a. LINC00346 and miRNA binding site prediction; b. MS2-RIP experiments verify LINC00346 can pull down miRNAs; c. Pull -down experiments verify LINC00346 adsorbed miRNAs; d. Double fluorescence reporter gene experiments miR-34a and LINC00346 directly Combining; e. AGO2 RIP experiments verify that miR-34a can pull down LINC00346; f. WB shows that miR-34a can rescue the regulation of protein levels of Notch1, CD44 or AXL by LINC00346; g. Tranwell experiments show that miR-34a can rescue LINC00346 pairs Regulation of migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells; h. Dual fluorescence reporter gene experiments show that miRNA can directly bind to the 3'UTR of Notch1, CD44 or AXL genes; i. In situ hybridization experiments show that LINC00346 and miR-34a can colocalize in cytoplasm in.
to sum up
This study reveals a potential new mechanism in the development of gastric cancer through bioinformatics analysis, functional experiments and molecular mechanism exploration techniques: during the development of gastric cancer, the transcription factors KLF5 and MYC bind to the promoter region of LINC00346 and promote its expression; LINC00346, which is highly expressed in gastric cancer, is mainly localized in the cytoplasm and competitively adsorbs miR-34a-5p, inhibiting the regulation of miR-34a-5p on its downstream target genes (Notch1, AXL, and CD44), ultimately leading to gastric cancer. Deteriorating development. The pleiotropic effect of LINC00346 on the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer cells suggests that LINC00346 can be used as an effective therapeutic target for gastric cancer.
This study reveals a potential new mechanism in the development of gastric cancer through bioinformatics analysis, functional experiments and molecular mechanism exploration techniques: during the development of gastric cancer, the transcription factors KLF5 and MYC bind to the promoter region of LINC00346 and promote its expression; LINC00346, which is highly expressed in gastric cancer, is mainly localized in the cytoplasm and competitively adsorbs miR-34a-5p, inhibiting the regulation of miR-34a-5p on its downstream target genes (Notch1, AXL, and CD44), ultimately leading to gastric cancer. Deteriorating development. The pleiotropic effect of LINC00346 on the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer cells suggests that LINC00346 can be used as an effective therapeutic target for gastric cancer.
Full text link:
Https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0236-y
Https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0236-y
Cloud order related product recommendation:
Whole transcriptome sequencing
Circular RNA sequencing
LncRNA sequencing
M6A RNA whole transcriptome methylation sequencing
M5C RNA whole transcriptome methylation sequencing
m1A RNA whole transcriptome methylation sequencing
RNA pull down
RIP sequencing
Whole transcriptome sequencing
Circular RNA sequencing
LncRNA sequencing
M6A RNA whole transcriptome methylation sequencing
M5C RNA whole transcriptome methylation sequencing
m1A RNA whole transcriptome methylation sequencing
RNA pull down
RIP sequencing
Cloud order customers published sequencing articles:
1. Whole-genome and Transcriptome Sequencing of Prostate Cancer Identify New Genetic Alterations Driving Disease Progression
2, SUMOylation of the m6A-RNA methyltransferase METTL3 modulates its function
3, CircHLA-C Plays an Important Role in Lupus Nephritis by Sponging miR-150
4. Identification of Circular RNAs and Their Targets in Leaves of Triticum aestivum L. under Dehydration Stress
5, Circular RNA alterations are involved in resistance to avian leukosis virus subgroup-J-induced tumor formation in chickens
6. Identification of circular RNAs and their alterations involved in developing male Xenopus laevis chronically exposed to atrazine
7. Identification and characterization of circular RNAs in zebrafish
8. Differential Expression of Circular RNAs in Glioblastoma Multiforme and Its Correlation with Prognosis
9, Circular RNA Signature Predicts Gemcitabine Resistance of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcino
10, Circular RNA Vav3 sponges gga-miR-375 to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition
11. RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
12, Analysis of changes to lncRNAs and their target mRNAs in murine jejunum after radiation treatment
Circular RNA expression alteration in exosomes from the brain extracellular space after traumatic brain injury in mice
Shanghai Yunxu Biological Technology Co., Ltd.
Shanghai Cloud-seq Biotech Co., Ltd.
Address: 3rd Floor, Building 20, No. 518, Zhangzhu Road, Songjiang District, Shanghai
Telephone Fax Website:
mailbox:
2, SUMOylation of the m6A-RNA methyltransferase METTL3 modulates its function
3, CircHLA-C Plays an Important Role in Lupus Nephritis by Sponging miR-150
4. Identification of Circular RNAs and Their Targets in Leaves of Triticum aestivum L. under Dehydration Stress
5, Circular RNA alterations are involved in resistance to avian leukosis virus subgroup-J-induced tumor formation in chickens
6. Identification of circular RNAs and their alterations involved in developing male Xenopus laevis chronically exposed to atrazine
7. Identification and characterization of circular RNAs in zebrafish
8. Differential Expression of Circular RNAs in Glioblastoma Multiforme and Its Correlation with Prognosis
9, Circular RNA Signature Predicts Gemcitabine Resistance of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcino
10, Circular RNA Vav3 sponges gga-miR-375 to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition
11. RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
12, Analysis of changes to lncRNAs and their target mRNAs in murine jejunum after radiation treatment
Circular RNA expression alteration in exosomes from the brain extracellular space after traumatic brain injury in mice
Shanghai Yunxu Biological Technology Co., Ltd.
Shanghai Cloud-seq Biotech Co., Ltd.
Address: 3rd Floor, Building 20, No. 518, Zhangzhu Road, Songjiang District, Shanghai

Telephone Fax Website:
mailbox:
Tylvalosin Tartrate,Tylvalosin Premix,Tylvalosin Veterinary Drug,Tylvalosin Tartrate Pig
Shandong Shengli Bioengineering Co., Ltd , https://www.shenglipharm.com