BACKGROUND INTRODUCTION
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is an idiopathic intestinal inflammatory disease involving the ileum, rectum, and colon. Clinical manifestations of diarrhea, abdominal pain, and even bloody stools. According to the location and severity of the disease, it can be divided into Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). IBD is closely related to the incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer. The etiology of IBD is complex and is currently thought to be related to genetic susceptibility, immune response disorders, and environmental factors. A large body of evidence suggests that intestinal microbes are also a key factor in the pathogenesis of IBD.
IBD patients are associated with intestinal flora imbalance, mucosal and fecal microbial diversity. Recent studies have shown that bifidobacteria abundance in the intestinal microbiota is associated with childhood IBD, while sulfite-reducing bacteria Bilophila wadsworthia is associated with the development of interleukin (IL)-10 deficient mice with colitis. Abundance will increase due to high milk fat intake.
It is a Solanaceae and a genus of the genus Solanaceae. It is mainly represented by Lycium barbarum L. and contains a variety of phytochemicals. Among them, Lycium barbarum polysaccharide (LBP) is the most important functional component. However, the current prebiotic efficacy of scorpion regulating intestinal flora is unclear.
In 2018, Yifei Kang and others at the Washington State University School of Food Science published a book entitled "Goji berry modulates gut microbiota and alleviates colitis in IL" in Molecular Nutrition & Food Research (IF=5.232, Food Science and Technology). -10-deficient mice" article.
Main method used
METHODS
1. Immunohistochemistry
2. Quantitative RT-PCR
3.16S rRNA qPCR in specific species
4. Short-chain fatty acid analysis: gas chromatography (GC)
5. Fecal IgA Analysis: Kit
ABSTRACT
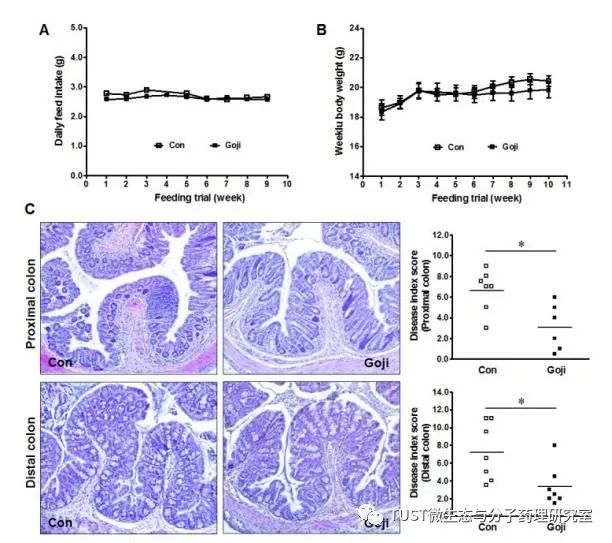
Scope of the study : This study examined the effects of scorpion on spontaneous colitis and its probiotic effects in interleukin (IL)-10 deficient mice.
METHODS: IL-10 deficient mice were randomized into standard feed (control group) and control diet supplemented with sputum (1% dry feed weight) for 10 weeks of continuous collection of colon tissue and feces.
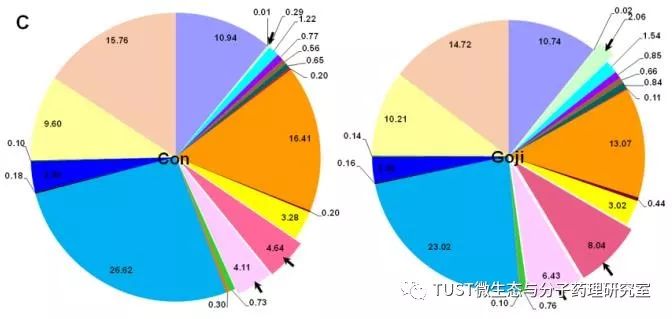
RESULTS: Scorpion could reduce the pathological biologic score of colon, decrease the expression of Il17a and Tgfb1 mRNA, and increase the expression of Muc1 and fecal IgA. Illumina MiSeq sequencing showed that the addition of scorpions increased the abundance of Actinobacteriaphylum, resulting in the proliferation of Bifidobacteria in the gut microbiota. In addition, under the Clostridium group XIVa, feeding cockroaches also promoted butyric acid-producing bacteria such as the Streptococcus lactis Ruminococcaceae family and Roseburia spp. In addition, the increase in Clostridium leptum and its major member Fecalibacterium prazusnitzii, which produces butyric acid, is also very pronounced. In addition, in the feces of the scorpion group, accompanied by an increase in the content of butyric acid, the expression of the butyryl-CoA transferase gene, a key enzyme for butyric acid production of butyric acid-producing bacteria, was also increased by a factor of six.
1)High-luminance and white LED, features in long life and good stability.
2)Large LCD screen, high luminance, abundant contents display, optional languages: Chinese and English.
3)User-friendly interface.
4)Optional units: international unit, conventional unit and symbol system.
5)Three working mode: one-step/slow/fast testing mode, suitable for different user group.
6)Monitoring the whole test process, auto-character and audible prompt.
7)Be compatible with 8, 10 and 11-parameter test strip.
8)Standard RS232 interface and interface for data communication.
9)Built-in thermal printer.
Urine Analyzer,Urine Analyser,At Home Water Test,Water Indicator Paper
Changchun LYZ Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.lyzinstruments.com